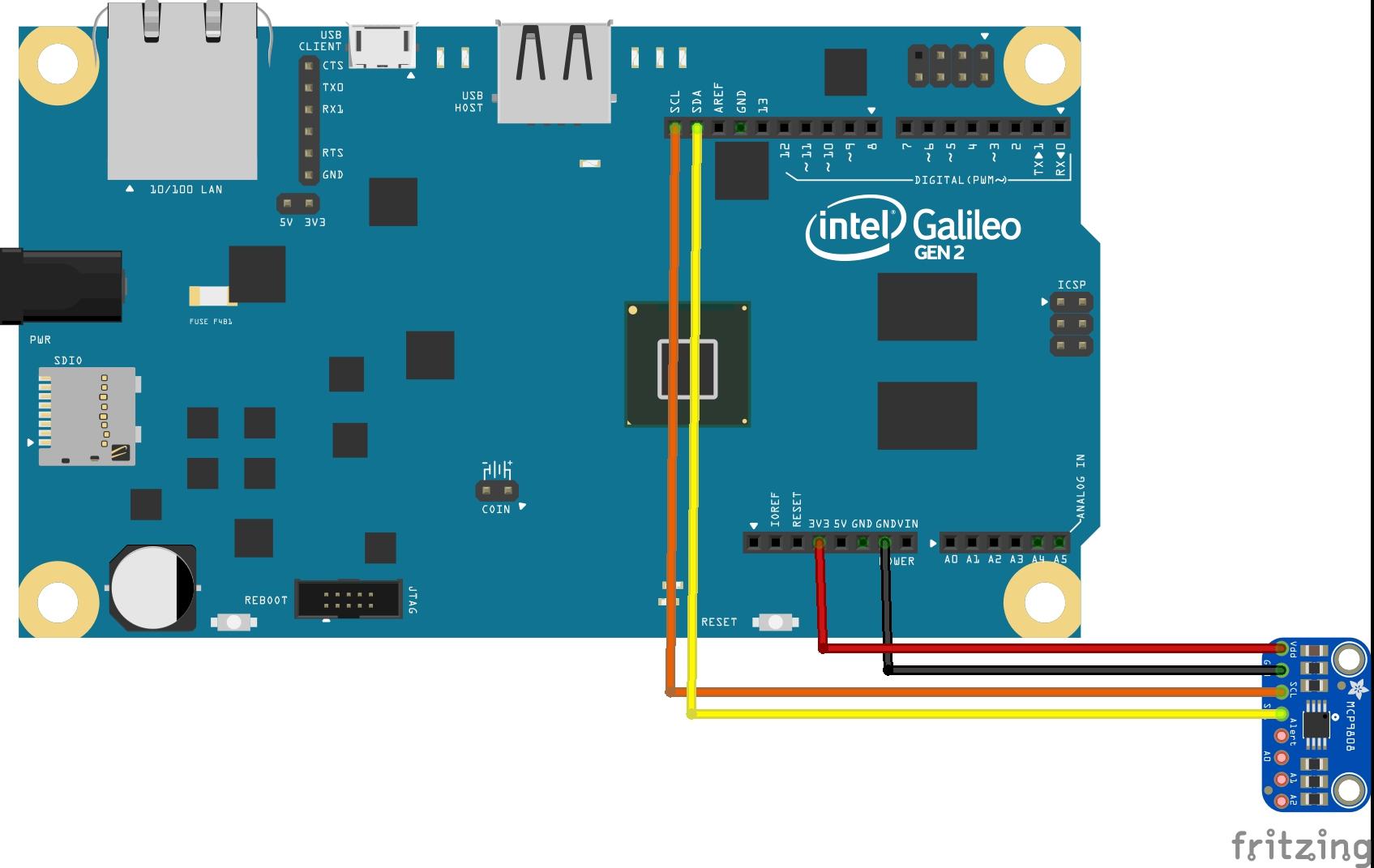
In this example we will connect up an MCP9808 sensor to our Intel Galileo
The MCP9808 digital temperature sensor converts temperatures between -20°C and +100°C to a digital word with ±0.5°C (max.) accuracy. The MCP9808 comes with user-programmable registers that provide flexibility for temperature sensing applications. The registers allow user-selectable settings such as Shutdown or low-power modes and the specification of temperature Event and Critical output boundaries. When the temperature changes beyond the specified boundary limits, the MCP9808 outputs an Event signal. The user has the option of setting the event output signal polarity as an active-low or active-high comparator output for thermostat operation, or as temperature event interrupt output for microprocessor-based systems.
The event output can also be configured as a Critical temperature output. This sensor has an industry standard 2-wire, SMBus and Standard I2C™Compatible compatible (100kHz/400kHz bus clock) serial interface, allowing up to eight sensors to be controlled in a single serial bus.
Features
-
-
- Accuracy:
- ±0.25°C (typical) from -40°C to +125°C
- ±0.5°C (maximum) from -20°C to +100°C
- User Selectable Measurement Resolution:
- 0.5°C, 0.25°C, 0.125°C, 0.0625°C
- User Programmable Temperature Limits:
- Temperature Window Limit
- Critical Temperature Limit
- User Programmable Temperature Alert Output
- Operating Voltage Range: 2.7V to 5.5V
- Operating Current: 200 µA (typical)
- Shutdown Current: 0.1 µA (typical)
- Accuracy:
-
Parts List
| Label | Part Type |
|---|---|
| Part1 | Intel Galileo Gen2 |
| Part3 | MCP9808 High Accuracy I2C Temperature Sensor |
Layout
An I2C sensor which is powered from 3.3v and Gnd so easy to connect up to the galileo as you can see below
Code
This is the default code example that comes with the Adafruit library – https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_MCP9808_Library
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <Wire.h>
#include "Adafruit_MCP9808.h"
// Create the MCP9808 temperature sensor object
Adafruit_MCP9808 tempsensor = Adafruit_MCP9808();
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("MCP9808 demo");
// Make sure the sensor is found, you can also pass in a different i2c
// address with tempsensor.begin(0x19) for example
if (!tempsensor.begin())
{
Serial.println("Couldn't find MCP9808!");
while (1);
}
}
void loop()
{
// Read and print out the temperature, then convert to *F
float c = tempsensor.readTempC();
float f = c * 9.0 / 5.0 + 32;
Serial.print("Temp: "); Serial.print(c); Serial.print("*C\t");
Serial.print(f); Serial.println("*F");
delay(1000);
}
[/codesyntax]
Testing
Open the serial monitor and you should see something like this
Temp: 28.44*C 83.19*F
Temp: 29.13*C 84.43*F
Temp: 29.75*C 85.55*F
Temp: 30.06*C 86.11*F
Temp: 30.44*C 86.79*F
Temp: 30.69*C 87.24*F
Temp: 30.81*C 87.46*F
Temp: 30.25*C 86.45*F
Temp: 29.88*C 85.78*F
Temp: 29.62*C 85.32*F