In this example we show how to connect a MAG3110 3D magnetic sensor to a MSP-EXP432P401R LaunchPad, the example will use the Energia IDE.
I used a MAG3110 module in this example, which you can see below
Connection
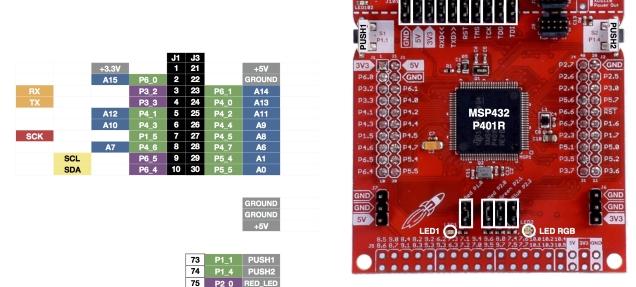
Here is a picture of the launchpad so you can see what pins we are referring to below in the table
| Module Connection | MSP432 Connection |
| SDA | J1-10 SDA |
| SCL | J1-9 SCL |
| Gnd | J3-22 Gnd |
| Vcc | J1-1 3.3v |
Code
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include<Wire.h>
// MAG3110 I2C address is 0x0E(14)
#define Addr 0x0E
void setup()
{
// Initialise I2C communication as MASTER
Wire.begin();
// Initialise serial communication, set baud rate = 9600
Serial.begin(9600);
// Start I2C Transmission
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select control register-1
Wire.write(0x10);
// Set active mode enabled
Wire.write(0x01);
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(300);
}
void loop()
{
unsigned int data[6];
// Start I2C Transmission
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select data register
Wire.write(0x01);
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
// Request 6 bytes of data
Wire.requestFrom(Addr, 6);
// Read 6 bytes of data
// xMag lsb, xMag msb, yMag lsb, y Mag msb, zMag lsb, zMag msb
if(Wire.available() == 6)
{
data[0] = Wire.read();
data[1] = Wire.read();
data[2] = Wire.read();
data[3] = Wire.read();
data[4] = Wire.read();
data[5] = Wire.read();
}
// Convert the data
int xMag = ((data[1] * 256) + data[0]);
int yMag = ((data[3] * 256) + data[2]);
int zMag = ((data[5] * 256) + data[4]);
// Output data to serial monitor
Serial.print("Magnetic field in X Axis : ");
Serial.println(xMag);
Serial.print("Magnetic field in Y Axis : ");
Serial.println(yMag);
Serial.print("Magnetic field in Z Axis : ");
Serial.println(zMag);
delay(1000);
}
[/codesyntax]
Output
Open the serial monitor and you should see something like this
Magnetic field in X Axis : 31230
Magnetic field in Y Axis : 32261
Magnetic field in Z Axis : 17665
Magnetic field in X Axis : 30974
Magnetic field in Y Axis : 32517
Magnetic field in Z Axis : 13057
Magnetic field in X Axis : 31742
Magnetic field in Y Axis : 31237
Magnetic field in Z Axis : 18177
Magnetic field in X Axis : 31486
Magnetic field in Y Axis : 32005
Magnetic field in Z Axis : 18689
Links
GY-3110 MAG3110 Triple 3 Axis Magnetometer Breakout Electronic Compass Sensor Module For Arduino